Smart Cities and Iot
Smart cities IoT are cities that use Internet of Things devices to improve infrastructure, public services and more.
Cities in the future can tackle various challenges like traffic, energy conservation, safety, and environmental monitoring, thanks to the widespread use of Internet of Things (IoT) technologies.
In this article, We will help you explore the concepts of IoT and Smart City.
What is the Internet of Things Smart Cities?
Internet of things smart cities are interconnected concepts which improve city life by using technology and data to make things work better, last longer, and be more eco-friendly.
Smart Cities: A smart city is an urban area that uses various types of electronic data collection sensors to supply information which is used to manage assets and resources efficiently.
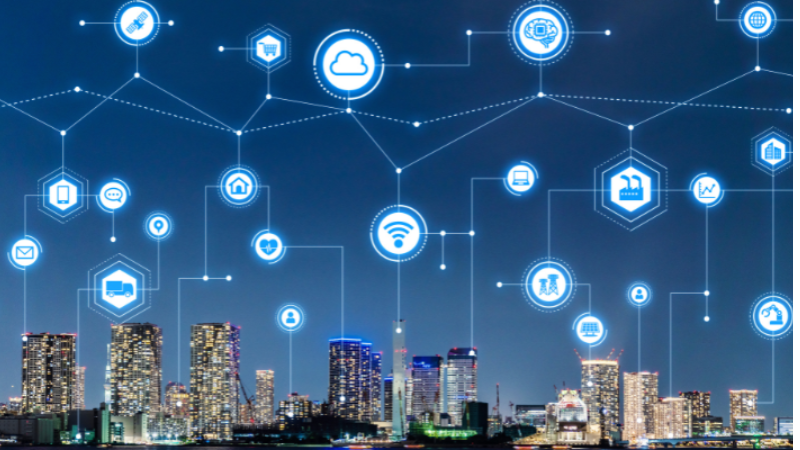

This includes data collected from citizens, devices, and assets that is processed and analyzed to monitor and manage traffic and transportation systems, power plants, water supply networks, waste management, law enforcement, schools, libraries, hospitals, and other community services.
The overarching goal is to advance the quality of life for citizens, improve the sustainability of urban living, and drive economic growth.
Internet of Things (IoT): IoT means connecting physical objects like devices and sensors to share data over the internet. In smart cities, IoT is important for linking different systems and devices to collect, analyze, and respond to data quickly.
For example, IoT sensors can monitor air quality, traffic flow, energy usage, and other environmental factors, providing valuable insights for city planners and administrators to make informed decisions and optimize resource allocation.
In essence, the convergence of smart cities and IoT leverages technology to transform traditional urban environments into more connected, efficient, and sustainable communities that better serve the needs of their inhabitants.
What is the Difference Between Digital City, Sustainable City, Smart Cities IoT?
The question is a legitimate one, because the three terms can cause some confusion, or be used as synonyms when this is not exactly the case.
Digital CIty
A digital city is a place where technology is used to handle lots of data and connect different devices through the Internet of Things (IoT). This helps provide people with better and more useful services for managing and using the city environment.
Sustainable City
A sustainable city, on the other hand, brings together the concept of safety, inclusiveness and durability, with a focus on reducing pollution, shifting from a linear to a circular economy and enhancing cultural and landscape heritage.
Smart City
The smart city, then, is nothing more than the fusion of a digital city and a sustainable city, because it uses technology to improve the urban environment, transportation and infrastructure with the aim of protecting and improving the lives of citizens and the environment in every aspect.
10 IoT Smart City Examples
Here are 10 examples of IoT implementations in smart cities:
Smart Transportation
IoT in cities use sensors integrated into roads, traffic lights, and vehicles work together to optimize transportation networks. These sensors collect real-time data on traffic flow, vehicle speeds, and road conditions, allowing traffic signals to adjust dynamically to reduce congestion and improve traffic flow.
Additionally, IoT-powered navigation systems provide drivers with real-time route guidance, helping them avoid traffic jams and choose the most efficient paths.
Smart transportation systems also include initiatives like dynamic toll pricing, where toll rates vary based on traffic conditions to manage congestion.
Smart Energy Management
IoT devices are important in optimizing energy usage within smart cities.
Smart meters installed in homes and businesses track energy consumption in real-time, allowing residents and utility providers to identify opportunities for energy conservation and cost savings.
Building management systems equipped with IoT sensors monitor occupancy levels, lighting, and HVAC (Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning) systems to adjust energy usage based on demand and occupancy patterns, resulting in significant energy savings and reduced environmental impact.
Waste Management – IoT Smart City Examples
IoT-enabled trash bins equipped with fill-level sensors and GPS trackers monitor waste levels and location in real-time. When bins reach a certain capacity, they automatically trigger alerts for waste collection teams, optimizing collection routes and reducing unnecessary trips.
Additionally, IoT sensors can detect unusual waste patterns, such as illegal dumping or hazardous materials, allowing authorities to take prompt action to mitigate environmental risks and ensure proper waste disposal.
Air Quality Monitoring
IoT sensors deployed throughout the city continuously monitor air quality parameters such as particulate matter, ozone levels, and carbon monoxide concentrations.
This data is collected and analyzed in real-time to generate air quality indices, which are shared with the public through mobile apps and websites.
City officials can use this information to implement targeted interventions, such as traffic rerouting or emission controls, to improve air quality and protect public health.
Water Management
IoT sensors deployed in water distribution networks detect leaks, monitor water pressure, and measure water quality parameters such as pH levels and chlorine concentration. By continuously monitoring these metrics, utilities can identify and repair leaks quickly, minimize water loss, and ensure safe drinking water supplies for residents.
Additionally, smart irrigation systems equipped with IoT sensors adjust watering schedules based on weather forecasts and soil moisture levels, conserving water and promoting sustainable landscaping practices.
Smart Lighting
IoT-connected streetlights equipped with motion sensors and dimming capabilities adjust lighting levels based on environmental conditions and pedestrian or vehicular traffic.
During periods of low activity, such as late at night or in areas with few pedestrians, streetlights can dim to conserve energy.
Conversely, in high-traffic areas or during emergencies, lights can brighten automatically to improve visibility and safety.
Additionally, IoT-enabled lighting systems can be remotely monitored and managed, allowing maintenance teams to identify and repair faulty lights more efficiently.
Public Safety and Security
IoT devices such as surveillance cameras, gunshot detectors, and emergency call boxes improve public safety by providing real-time monitoring and response capabilities to law enforcement agencies.
Surveillance cameras equipped with advanced analytics can detect suspicious behavior or objects and alert authorities immediately.
Gunshot detection systems use acoustic sensors to identify and locate gunshots in urban environments, enabling rapid deployment of emergency responders.
Emergency call boxes equipped with IoT sensors provide a direct line of communication to emergency services, allowing individuals to request assistance quickly in case of emergencies.
Smart Buildings
IoT sensors and systems integrated into buildings monitor various parameters such as occupancy levels, temperature, humidity, and air quality.
Building management systems analyze this data to optimize energy usage, HVAC systems, and lighting based on occupancy patterns and environmental conditions.

Additionally, IoT-enabled maintenance systems perform predictive maintenance tasks, identifying potential equipment failures before they occur and minimizing downtime.
Health Monitoring
IoT-enabled healthcare devices and wearables monitor vital signs, track physical activity, and provide remote patient monitoring capabilities. Also, you can read more about IoT medicine.
These devices collect real-time health data, such as heart rate, blood pressure, and blood glucose levels, allowing individuals and healthcare providers to monitor and manage chronic conditions more effectively.
Remote patient monitoring systems equipped with IoT sensors enable healthcare professionals to monitor patients’ health status from a distance, reducing the need for frequent in-person visits and improving access to healthcare services, especially in underserved areas.
Urban Agriculture
IoT technology is revolutionizing urban agriculture by enabling efficient monitoring and management of urban farming initiatives.
By offering real-time environmental data, soil moisture sensors, and weather stations empower farmers to optimize irrigation schedules and conserve water resources effectively. This technology enhances agricultural efficiency and sustainability while ensuring optimal crop growth.
Crop monitoring platforms equipped with IoT sensors detect pest infestations and nutrient deficiencies early, enabling timely interventions to prevent crop damage and improve yields.
Additionally, vertical farming systems utilize IoT-controlled LED lighting and hydroponic systems to maximize space efficiency and produce high-quality crops year-round in urban environments.
Summary of Smart Cities IoT
Smart cities IoT facilitates the connection and administration of infrastructure, municipal services, and public amenities. This encompasses various applications such as smart lighting, waste management, connected public transportation, and security solutions, highlighting a wide array of uses.
Smart city IoT solutions, despite their diversity, have common benefits such as lower energy costs and more efficient use of resources. Finally, they help to contribute to safer urban areas and a healthier environment.
F.A.Q
What are Smart Cities IoT❓
Smart cities use IoT devices to improve infrastructure and public services by connecting and managing various systems and devices through technology and data.
How do IoT and Smart Cities Work Together❓
IoT sensors collect data from different city systems and devices, enabling real-time analysis and decision-making to optimize resource allocation and improve urban life.
What Benefits Do Smart Cities IoT Solutions Bring❓
Smart cities using IoT solutions lead to reduced energy costs, optimized use of natural resources, safer cities, and healthier environments by leveraging technology and data-driven approaches.
What Examples Illustrate Smart Cities IoT Implementations❓
Examples include smart transportation systems, energy management, waste management, air quality monitoring, water management, smart lighting, public safety, smart buildings, health monitoring, and urban agriculture.
What's the Difference Between Digital City, Sustainable City, and Smart City❓
A digital city manages data and communication via IoT, a sustainable city focuses on reducing pollution and promoting durability, while a smart city combines both digital and sustainable aspects to enhance citizens’ lives and the environment.